Artificial muscle for soft robotics: Low voltage, high hopes
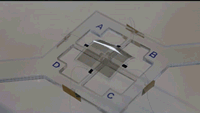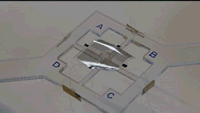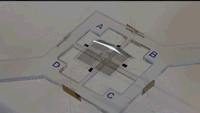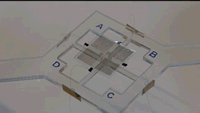 Phys.org: Soft robots do a lot of things well but they're not exactly known for their speed. The artificial muscles that move soft robots, called actuators, tend to rely on hydraulics or pneumatics, which are slow to respond and difficult to store.
Phys.org: Soft robots do a lot of things well but they're not exactly known for their speed. The artificial muscles that move soft robots, called actuators, tend to rely on hydraulics or pneumatics, which are slow to respond and difficult to store.
Dielectric elastomers, soft materials that have good insulating properties, could offer an alternative to pneumatic actuators but they currently require complex and inefficient circuitry to deliver high voltage as well as rigid components to maintain their form—both of which defeat the purpose of a soft robot.
Now, researchers at the Harvard John A. Paulson School of Engineering and Applied Sciences (SEAS) have developed a dielectric elastomer with a broad range of motion that requires relatively low voltage and no rigid components. They published their work recently in Advanced Materials. Cont'd...
Featured Product

