Deep learning opens up new fields of application for industrial image processing, which previously could only be solved with great effort or not at all. The new, fundamentally different approach to classical image processing causes new challenges for users.
 AI for All - All-in-one Solution Makes the Technology User-friendly
AI for All - All-in-one Solution Makes the Technology User-friendly

Article from | IDS Imaging Development Systems
Computer vision and image processing have become indispensable tools in various fields. Image processing systems are increasingly confronted with a constantly growing variety of products and variants and organic objects such as fruit, vegetables or plants. Conventional approaches with rule-based image processing quickly reach their limits if the image data to be analyzed varies too frequently and the differences are difficult or impossible to describe using algorithms. In such cases, a robust automation is not feasible due to an inflexible set of rules. Even if the task is supposed to be easy for people to solve. As an example, a child is able to recognize a car even if it has never seen the special model before. It is sufficient if the child has seen enough other car models previously.
Through machine learning, the ability to make flexible and independent decisions can now also be transferred to image processing systems. Using neural networks and deep learning algorithms, we can teach a computer to see objects, recognize them, and draw conclusions from what it has learned. Like a human being, such an "intelligent automation" learns and decides on empirical values.
Differences to classical image processing
The main difference to rule-based image processing is how and by whom image characteristics are identified and how the learned knowledge is represented. With the classical or "symbolic approach" an image processing specialist is responsible for selecting the image features that are decisive and describing them according to certain rules. Many lines of source code are required to specify in detail how to solve a given task. Because the software can only recognize what the rules cover. The subsequent execution takes place within defined limits without any room for interpretation. The actual intellectual achievement therefore lies solely with the image expert.
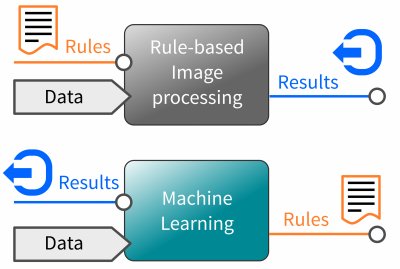
Figure 1 Machine learning allows a machine to teach things through examples rather than through many instructions.
The procedure for working with neural networks is quite different. Their advantage is to learn independently which image characteristics are important in order to draw the right conclusion. We then speak of a "non-symbolic approach", since the knowledge is only implicit and does not allow any insights into the solutions learned. Which characteristics are stored, how they are weighted and which conclusions are drawn is only affected by the quantity and content of the training images. Deep learning algorithms recognize and analyze the complete image content and relate the recognized characteristics to the "terms" to be learned, depending on the frequency of occurrence. The statistical frequency produces what we call experience during training. Google's artificial intelligence specialist Cassie Kozyrkov describes Machine Learning as a programming tool at this year's WebSummit 2019 in Lisbon. It allows to teach a machine things by examples rather than by many instructions.
The development of machine vision applications based on AI therefore requires a rethink. It is important to understand that the quality of the results - i.e. the speed and reliability of object detection - depends on what a neural network detects and concludes. Here the knowledge of the respective professional plays a very decisive role, who must provide the necessary data sets for the training with as many different example pictures as possible including the terms to be learned. The responsibility for the classical approach, which lay with an image processing specialist, is taken over by a data specialist in machine learning.
New challenges
But which (new) skills are needed to bring machine learning into your own company? Breaking down the development of an AI application into individual steps actually reveals tasks and concepts that are completely new to learn compared to the classical approach. The handling and preparation of image data as well as training neural networks require completely new tools and development frameworks, which must be installed and executed on a suitable PC infrastructure. Although necessary instructions and open source software are usually freely available from cloud providers or on platforms such as Github, they only provide the fundamental basic tools which require a high degree of experience. And not only the creation, but also the execution and evaluation of the training results on an appropriate hardware platform requires understanding and knowledge of hardware, software and their interfaces.
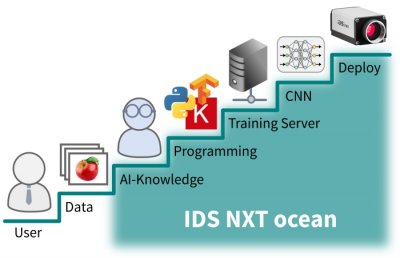
Figure 2 IDS NXT ocean lowers the entry barrier with easy-to-use tools.
Start immediately with the machine learning all-in-one solution
IDS would like to support the user right from the first steps with the new technology. IDS combines deep learning experience and camera technology with an all-in-one inference camera solution. This enables every user to start immediately with AI-based image processing. With IDS NXT ocean, IDS lowers the entry barrier and provides easy-to-use tools for creating inference tasks in a few minutes without much prior knowledge and executing them immediately on a camera.
The concept is based on three important components:
- An easy to use training software for neural networks
- and an intelligent camera platform
- including an AI accelerator that executes the neural networks on the hardware side.
All components have been developed directly by IDS and are designed to work together perfectly. This makes it very easy for the user and the overall system very powerful.
The cloud-based training software IDS NXT lighthouse leads step-by-step through data preparation to the training of artificial intelligence in the form of a neural network. The user never gets in contact with any basic tools or has to deal with the installation of development environments. As a web application, IDS NXT lighthouse is immediately ready for use. The user has sufficient storage space and training performance for all his projects in an easy-to-use workflow. Log in, upload training images, label and then train the desired net. Customers benefit from the data center and network architecture of German servers operated by Amazon Web Services (AWS), which is specifically designed to meet the highest standards of data protection and security.
With a few configuration settings, the user specifies the speed and accuracy requirements for his application in simple dialogs. IDS NXT lighthouse then selects the network and sets up the necessary training parameters completely independently. The training results already give the user a good prediction about the quality of the trained intelligence and thus enable quick modification and repetition of the training process. The system is continuously improved and upgraded. Without having to plan for updates and maintenance phases, the latest version of the software is always available to everyone. The user can concentrate completely on solving his application without having to build up the knowledge about learning methods and artificial intelligence himself.
The manufacturer uses supervised learning at IDS NXT lighthouse to train neural networks. The Deep Learning algorithms learn with predefined pairs of inputs and outputs. The teacher - in this case the user - have to provide the correct function value for an input during learning by assigning the correct class to a picture example. The network is trained to be able to make associations independently by making predictions regarding image data in the form of percentages. The higher the value, the more accurate and reliable the prediction.
The seamless interaction of the software with the IDS NXT camera families rio & rome ensures a quick success. Because fully trained neural networks can be uploaded and executed directly and without programming effort on one of these cameras. Thus, the user immediately has a completely working embedded vision system that sees, recognizes and derives results from captured image data. With its digital interfaces, even machines can be controlled directly.
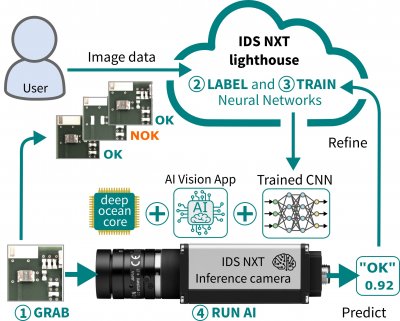
Figure 3 Seamless interaction of software and hardware for quick success
Embedded Vision Hybrid System
IDS has developed its own AI core for the FPGA of the intelligent IDS NXT camera platform called "deep ocean core", which executes pre-trained neural networks hardware-accelerated. This turns the full-fledged industrial cameras into high-performance inference cameras that make artificial intelligence useful in industrial environments. Image analysis is performed decentralized, avoiding bandwidth bottlenecks during transmission. Cameras based on the IDS NXT platform can thus keep pace with modern desktop CPUs in terms of accuracy and speed of results - with significantly less space and energy consumption at the same time. The reprogrammability of the FPGA offers additional advantages in terms of future security, low recurring costs and time-to-market.
The perfect adaptation of IDS' own software and hardware allows the user to choose the target inference time before training. IDS NXT lighthouse then ensures optimal training settings while considering the AI core performance of the camera. Thus the user expects no surprises during the subsequent execution of the inference, eliminating the need for time-consuming readjustment and re-training. Once integrated, the IDS NXT system remains 100% compatible and consistent in its behavior for the user. Especially with industrially certified applications this is a significant advantage.
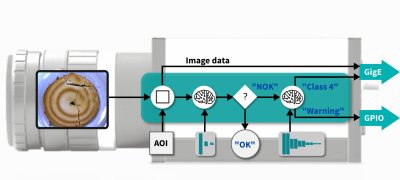
Figure 4 The functionality of IDS NXT inference cameras will be extendable with apps and CNNs as required.
Due to the powerful hardware, the Embedded Vision platform is much more than just an inference camera used to execute neural networks. The feature set of the CPU-FPGA combination will be extendable by the user according to his needs in the next development step using vision apps. Recurring vision tasks can then be set up and changed quickly. Even a completely flexible image processing sequence can then be realized. Captured images are first preprocessed, for example, before a quite simple and fast classification sorts good and bad parts. If errors occur, a much more complex neural network can be reloaded in milliseconds to determine the error class in much more detail and transfer the results to a database. Customized solutions can then be easily implemented using an app development kit. Users can then create their own individual vision apps in just a few steps and install and run them on IDS NXT cameras.
IDS NXT cameras are designed as hybrid systems to enable both pre-processing of image data with classical image processing and feature extraction using neural networks side by side to efficiently run image processing applications on a single device.
The content & opinions in this article are the author’s and do not necessarily represent the views of RoboticsTomorrow

IDS Imaging Development Systems Inc.
World-class image processing and industrial cameras "Made in Germany". Machine vision systems from IDS are powerful and easy to use. IDS is a leading provider of area scan cameras with USB and GigE interfaces, 3D industrial cameras and industrial cameras with artificial intelligence. Industrial monitoring cameras with streaming and event recording complete the portfolio. One of IDS's key strengths is customized solutions. An experienced project team of hardware and software developers makes almost anything technically possible to meet individual specifications - from custom design and PCB electronics to specific connector configurations. Whether in an industrial or non-industrial setting: IDS cameras and sensors assist companies worldwide in optimizing processes, ensuring quality, driving research, conserving raw materials, and serving people. They provide reliability, efficiency and flexibility for your application.
Other Articles
High-precision process monitoring and error detection in additive manufacturing
Inspection of critical infrastructure using intelligent drones
Multi-camera system with AI and seamless traceability leaves no chance for product defects
More about IDS Imaging Development Systems Inc.
Featured Product

