The opportunities within the Food Robotics market are vast, with potential for substantial advancements in robotic systems that can handle delicate food items, improve packaging efficiency, and innovate food assembly processes.
 Food Robotics - Transforming the Future of Food Processing
Food Robotics - Transforming the Future of Food Processing

Mr. Yogesh Shinde, ICT Manager | Market.us
Food robotics involves the application of robotic systems to various processes within the food industry, encompassing tasks from food processing and packaging to serving and preparation. These robots are designed to automate repetitive tasks, enhance efficiency, reduce operational costs, and improve the precision and hygiene of food handling. The Food Robotics market is expanding as industries seek innovative solutions to streamline production, address labor shortages, and meet stringent safety regulations.
According to a recent report by Market.us, the Global Food Robotics Market is expected to reach approximately USD 8.9 Billion by 2033, ascending from USD 3.0 Billion in 2023, at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 11.5% during the forecast period from 2024 to 2033.
The market for food robotics is witnessing substantial growth driven by several key factors. The increasing demand for packaged foods, rising food safety standards, and the need for more efficient production lines are primary growth drivers. Additionally, the technological advancements in robotic systems, such as enhanced sensors, machine learning, and artificial intelligence, are enabling more complex tasks to be automated, further fueling market expansion.
Demand for food robotics is currently surging due to the global increase in food production and the need for automation to maintain consistent quality and safety standards. Industries are adopting robotic systems at a higher rate to cope with the challenges of labor shortages and to minimize human contact with food during processing and packaging, which is particularly significant in the wake of health crises like the COVID-19 pandemic.
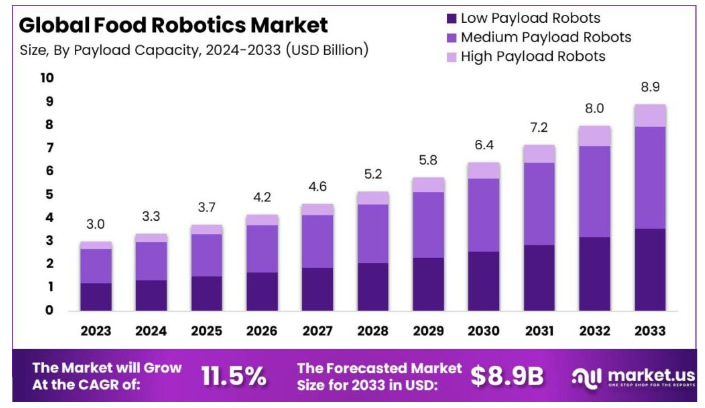
Figure 1: Illustrates a year-on-year growth trajectory for the Food Robotics market
Growth factors for the food robotics market include the rising labor costs and scarcity in many developed countries, which compel food processing industries to adopt automation. The push towards enhanced productivity and cost-effectiveness in food manufacturing also plays a crucial role in the adoption of robotics. Furthermore, consumer demands for quicker, safer, and more reliable food delivery systems contribute significantly to the growth of this sector.
The opportunities in the food robotics market are vast, ranging from the development of robots that can handle delicate food items without damage to innovations in robotic packaging and sorting systems. There is also potential for growth in emerging markets, where the adoption of automation in food processing is still in its early stages. As robotic technologies continue to evolve, their integration into more complex food preparation tasks presents significant opportunities for companies in the food industry to innovate and improve their operational efficiencies.
Food Robotics Statistics
-
Market Size: Projected to reach an impressive value of approximately USD 8.9 Billion by 2033, up from USD 3.0 Billion in 2023, exhibiting a robust compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 11.5% during the forecast period from 2024 to 2033.
-
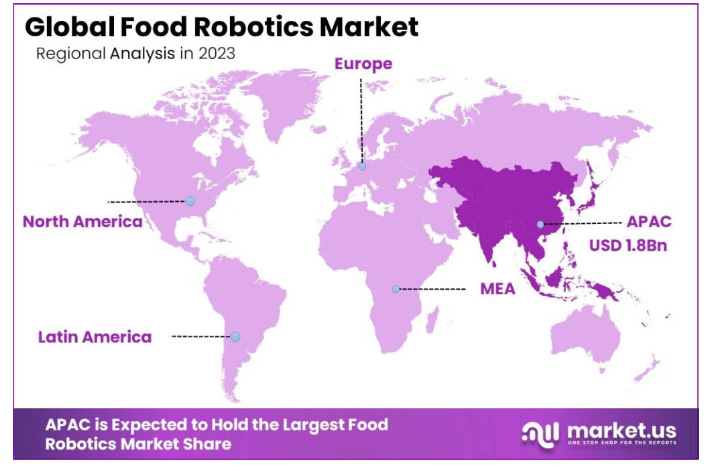
Regional Landscape (2023): Asia-Pacific stands out as a significant leader within the food robotics market, securing a commanding share of 42.7%, translating to revenues of USD 1.8 billion.
-
Robot Types: The Articulated Robots segment has maintained a leading position in the market, holding a share of 34.9% in 2023.
-
Payload Capacity: Medium Payload Robots dominated the market, capturing a substantial 49.1% share in 2023.
-
Application Areas: The Palletizing function emerged as a major segment, accounting for 25.5% of the market share in 2023.
-
Industry Segments: Beverages Companies represented a significant portion of the market, with a dominance of over 23% in 2023.
-
Industrial Automation Trends: Approximately 88% of companies have signaled their intentions to enhance their operational frameworks by integrating robotics. This strategic inclination underscores a broader trend of automation across various sectors.
-
Global Deployment of Industrial Robots: As of now, the global deployment stands at an estimated 3 million units, marking significant penetration in manufacturing and related industries.
-
Annual Market Additions: On an annual basis, the market welcomes approximately 400,000 new robots, reflecting robust growth and the ongoing evolution of technological capabilities within the sector.
-
Industrial Robotics Market Value: Financially, the industrial robotics market is valued at approximately $43.8 billion in revenue.
Food Robotics Market in Asia-Pacific
In 2023, Asia-Pacific held a dominant market position in the Food Robotics Market, capturing more than a 42.7% share with revenues amounting to USD 1.8 billion. This region leads due to several factors, including rapid industrialization, increased investments in automation technologies, and a growing food processing industry. Countries such as China, Japan, and South Korea are at the forefront, heavily investing in robotics to enhance productivity and efficiency in food manufacturing and processing.
The emphasis on improving food safety standards and reducing labor costs has also propelled the adoption of robotics in this region. With high labor costs in developed Asian economies and labor shortages in emerging ones, food producers are increasingly turning to robotic solutions. These solutions not only address workforce challenges but also improve precision and consistency in food production, which is crucial for maintaining quality standards.
Furthermore, government initiatives across the region support the integration of advanced technologies in the food sector. For instance, China’s Made in China 2025 initiative explicitly aims to upgrade the country's manufacturing base by developing high-tech industries including robotics used in food production. Such policies underscore a regional commitment to technological adoption, which enhances the growth prospects of the food robotics market.
In contrast, North America and Europe also show significant market activity but have different growth dynamics. North America’s market expansion is driven by the increasing demand for packaged foods and the presence of major food production companies that are early adopters of automation technologies. Europe’s market growth is supported by stringent food safety regulations that encourage the adoption of advanced technologies to ensure compliance and traceability throughout the food supply chain.
Figure 2 : Food Robotics Market in Asia-Pacific
How to Implement AI Strategies for Food Robotics?
Market.us forecasts that the Artificial Intelligence Market size is expected to be worth around USD 2,745 billion by 2032, from USD 177 Billion in 2023, growing at a CAGR of 36.8% during the forecast period from 2024 to 2033.
Implementing AI strategies in food robotics can significantly enhance efficiency, quality control, and sustainability within the food industry. Here's a comprehensive guide on how to effectively integrate AI into food robotics:
-
Quality Control and Efficiency: AI can dramatically improve the precision of operations in food production. Through the use of sensors and cameras combined with machine learning algorithms, AI systems can identify defects or contaminants, ensuring only high-quality products reach consumers. This technology not only boosts production efficiency by optimizing resource allocation and production schedules but also enhances food safety by providing real-time monitoring capabilities.
-
Predictive Maintenance and Supply Chain Optimization: AI facilitates predictive maintenance by monitoring equipment and alerting operators to potential breakdowns before they occur, thereby reducing downtime. Additionally, AI improves supply chain management by analyzing historical and real-time data to forecast demand, optimize inventory, and enhance logistics planning. This can lead to reduced waste and more efficient use of resources.
-
Integration Challenges and Workforce Development: The integration of AI into existing systems can be challenging, often requiring upgrades to legacy systems. Additionally, there is a significant demand for a skilled workforce proficient in AI and robotics technologies. Companies need to invest in training and development to build this expertise internally​.
-
Ethical and Regulatory Considerations: When implementing AI, it is crucial to address ethical concerns, such as algorithmic bias and data privacy. Ensuring compliance with food safety regulations and maintaining transparent processes is also vital for consumer trust and regulatory compliance.
-
Leveraging AI for Personalization and Sustainability: AI enables the customization of food products to meet individual dietary needs and preferences. It also supports sustainable practices by analyzing data related to energy consumption and waste management, thus helping companies reduce their environmental impact.
-
Real-World Applications: Several companies are successfully using AI to streamline operations and improve product offerings. For example, Coca-Cola uses AI for efficient supply chain management, while Starbucks leverages AI for customer personalization in its app. These applications highlight AI’s potential to transform the food industry by making it more consumer-centric and efficient.
Recent Developments
-
Yaskawa Electric Corporation: In 2023, Yaskawa expanded its stake in Doolim-Yaskawa Co., Ltd., a South Korean company specializing in robotic painting and sealing systems. This move strengthens Yaskawa's position in the food robotics market, particularly in the development of robots for food packaging and processing applications.
-
OMRON Corporation: In 2023, OMRON Corporation enhanced its partnership with IBM Japan to advance data-driven corporate management. This collaboration aims to leverage OMRON's robotics technology in conjunction with IBM's data analytics capabilities, which is expected to have significant implications for the food robotics sector, particularly in optimizing production processes and ensuring quality control.
-
ABB Group: In March 2023, ABB announced the expansion of its North American robotics headquarters and manufacturing facility in Auburn Hills, Michigan. This expansion, expected to be completed by November 2023, represents a $20 million investment. The project will create 72 new jobs and enhance ABB's capacity to meet the growing demand for robotics solutions in sectors like food and beverage, healthcare, and packaging.
Emerging Trends in Food Robotics
-
Autonomous Mobile Robots (AMRs): AMRs are enhancing operational efficiencies across various sectors, including food services, by automating tasks such as delivery and bussing with advanced navigation capabilities​.
-
Robotics as a Service (RaaS): This model is becoming popular, offering robotic solutions on a subscription basis, which lowers the barrier to entry for businesses to adopt high-tech robotics without significant upfront investment.
-
Enhanced Ease of Use: Developments in robotics technology have led to more user-friendly interfaces that require minimal programming skills, broadening the accessibility of robotics across different levels of technical expertise.
-
Integration with AI and Digital Automation: Robots are increasingly integrated with AI, improving their adaptability and functionality in unpredictable environments, which is crucial for tasks like inventory management and customer service in the food industry​.
-
Sustainability Through Second-Life Applications: There is a growing trend towards refurbishing and reusing industrial robots, aligning with sustainability goals by extending the life cycle of these machines and supporting the circular economy.
Top Use Cases for Food Robotics
-
Cooking and Food Preparation: Robots are increasingly used in cooking and preparing meals, ensuring consistency and efficiency while reducing labor costs​.
-
Ordering and Payment Automation: Implementations of mobile and tabletop solutions for ordering and payments streamline operations and enhance customer service by reducing wait times and errors.
-
Inventory and Supply Chain Management: Robotics technology is applied in managing inventories and logistics, particularly in tracking and handling stock to reduce waste and improve supply chain efficiency​.
-
Cleaning and Sanitation: Robots equipped with specialized tools for cleaning are employed in maintaining hygiene and sanitation standards, crucial for food safety​.
-
Customer Service and Interaction: Food service robots are being deployed for customer interaction roles, such as greeting guests or serving food, enhancing the dining experience and operational efficiency.
Technological Innovations in Food Robotics
Technological innovations in the food robotics market have been accelerating, driven by demands for efficiency, safety, and adaptability in food production and service. Here are some key trends and innovations shaping this sector:
-
Increased Automation and Autonomy: Robotics technology has evolved beyond basic tasks to more complex operations like entire meal preparation. This shift is not only about automating single tasks but moving towards fully automated systems that can handle complex sequences of tasks across the food and beverage value chain​.
-
Adaptive Robotics: Modern food robotics emphasize flexibility, with systems designed to adapt quickly to changes in production demands or food safety standards. This includes software-based robotics that can modify their operations in real time, enhancing scalability and operational efficiency.
-
Sustainability in Food Production: Technological advancements are increasingly driven by the need for sustainable food production methods. This includes the development of 3D-printed food and lab-grown meat, which aim to reduce the environmental impact of traditional food production methods.
-
Advancements in Robotics Design: The design of food robots now often includes features to handle delicate tasks with precision, such as sorting and packaging, using medium payload robots that offer a good balance between flexibility and capacity.
-
Emergence of No-Code Robotic Systems: The adoption of "no-code" robotic systems is growing, allowing users to configure and deploy robots without the need for specialized programming skills, thus lowering barriers to adoption in the food industry.
-
Collaborative Robots (Cobots): Cobots continue to be a significant trend, particularly in environments requiring flexibility and safety. These robots work alongside human workers, capable of operating in diverse environmental conditions and are easily integrated into existing production lines.
Conclusion
In conclusion, The Food Robotics market is poised for significant expansion, driven by advancements in technology and increasing demands within the food industry. This growth is underpinned by the integration of automation technologies such as artificial intelligence, machine learning, and advanced sensor technology, which enhance the capabilities of robots in food processing and packaging. These technologies facilitate high levels of food safety, improve traceability, reduce waste, and optimize business processes, ultimately boosting operational productivity.
The opportunities within the Food Robotics market are vast, with potential for substantial advancements in robotic systems that can handle delicate food items, improve packaging efficiency, and innovate food assembly processes. Emerging markets also present significant opportunities as the adoption of food robotics is still in its early stages in these regions, signaling room for growth as industries begin to recognize the efficiency and safety benefits of robotic integration.
Mr. Yogesh Shinde is ICT Manager at Market.us. He oversees a comprehensive portfolio of ICT products and solutions, including network infrastructure, cybersecurity tools, cloud services, data center solutions, telecommunications equipment, software-defined networking (SDN), and Internet of Things (IoT) devices. With a focus on driving digital transformation and enhancing connectivity, Yogesh ensures that the company's offerings meet the evolving needs of both industrial and commercial sectors. His expertise in information and communication technology is instrumental in delivering innovative and reliable solutions to clients worldwide.
The content & opinions in this article are the author’s and do not necessarily represent the views of RoboticsTomorrow
Featured Product