Humanoid Robots: Large opportunity but limited uptake in the short- to mid-term
Humanoid robots have been all over the media over the past year, with significant enthusiasm from investors. Indeed, the total addressable market (TAM) for humanoid robots is vast, with a market potential of 25 million units shipped per year, equating to an potential opportunity of $2 trillion annually. However, to what extent will this opportunity be penetrated in the short- to mid-term?
Our latest report explores the potential for humanoid robots through to 2032, examining the key barriers to entry currently limiting uptake, including regulations and safety standards, dexterity and productivity, battery life, price, and form-factors. We conclude that, while the market will grow quickly, market penetration will be very low. Our baseline scenario forecasts a market size for humanoid robots of $2 billion by 2032, equating to just over 40,000 units shipped in that year. To put this into perspective, just under 200,000 mobile robots in total were shipped in 2024, reaching a market size of $5 billion.
However, while our projections remain conservative, we performed a scenario-based analysis. Below we’ve outlined our three scenarios along with the assumptions that underpin them.
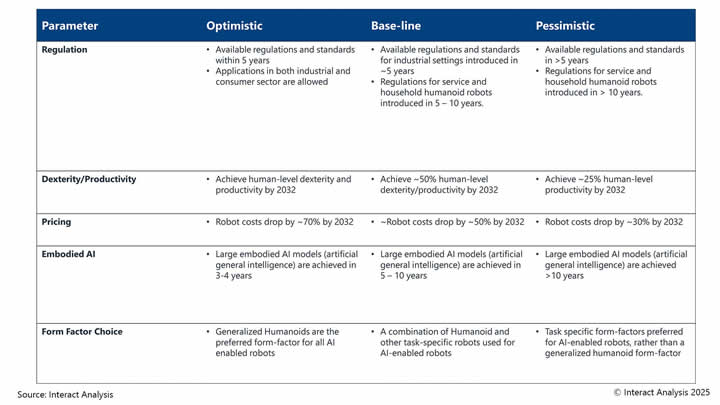
We have made our forecasts for the humanoid robot market through to 2032 based on optimistic, baseline and pessimistic scenarios

Our forecast for humanoid robot market growth sharply increases from 2029 onwards in all 3 scenarios
Where will we see humanoid robot deployments?
As part of our analysis, we captured the number of full-time equivalent (FTE) employees across different sectors and countries, and then assessed which specific workflows are substitutable with Humanoid Robots. For example, in the US there are approximately 15 million FTEs in manufacturing, comprising hundreds of specific roles (such as stock-takers, material movers, engineers, and technicians). Our analysis of the specific roles that constitute the US manufacturing sector suggests that 27% of the 15 million FTEs are directly substitutable with humanoid robots.
Performing this same analysis across four main industries (warehousing, manufacturing, service, and household), we were able to identify the true potential for humanoid robots. Our research reveals that manufacturing and service represent the largest total addressable market, although warehousing will see the greatest penetration given the suitability of workflows.
From a regional perspective, our analysis demonstrates that China will dominate uptake in the short- to mid-term. China’s generous subsidies and tax incentives, coupled with a more relaxed regulatory framework around humanoid deployments, is creating a conducive environment for humanoid robot manufacturers. The US is expected to lag behind China but remain the second largest market for humanoid robots. Europe, on the other hand, is predicted to see very few deployments due to more stringent labor laws and the strength of its unions; indeed, humanoid robots are job loss personified.
What components will be used in humanoids?
To date, the majority of components used to create humanoid robots have been developed in-house. The need for small, lightweight, and highly integrated components, yet with very high torque density, has necessitated in-house production. However, as the market matures and we see a gradual standardization of form-factors, components will shift to being off-the-shelf. As part of our research, we’ve assessed each major component, highlighting the key design trends required for component vendors to produce off-the-shelf products.
However, given the immaturity of the market, we’ve observed significant diversity in design trends with vendors opting for different design choices. While small humanoid robots often use planetary drives due to their lower torque and power needs, adult-height robots show greater variation. Many Chinese vendors favor high-speed motors with harmonic reducers for most joints, but for key areas like the hip, high-torque motors with planetary gearboxes are commonly chosen for their robustness and cost efficiency. Some manufacturers prioritize compact, low-torque, high-speed motors with high-reduction gearboxes, while others use quasi-direct actuators with low gear ratios (<10) or even gearless designs to enhance torque transparency and reduce friction. Additionally, cycloidal drives are emerging as an alternative, balancing torque transparency and payload capacity. As the humanoid robot industry matures, actuator designs are likely to evolve further, with no clear standard yet dominating the market.
Final thoughts
It’s clear that the opportunity for humanoid robots is large, but the significant amount of capital being invested into these companies shouldn’t be seen as an indication of market potential. In 2021, €5.5 billion was invested in rapid delivery companies, based on the thesis that all e-commerce deliveries would take place in less than two hours. This ended up being a false assumption and the majority of these companies are now either bankrupt or are operating with a valuation that’s a fraction of what it was.
It’s clear that humanoid robots are currently in a hype cycle and that history tells us that this will likely will collapse at some point, which is when the real test begins. Companies that have developed a strong product/market fit and are addressing the key issues around regulation and safety will likely remain, while those perpetuating the social media hype, and with fewer regulatory and safety credentials will likely fall by the wayside.
Featured Product

